OVULATORY AND ANOVULATORY CYCLES, CAUSES AND HOW TO IDENTIFY THEM
In this seminar we shall be discussing:
🛑 What is ovulation?
🛑 How does it occur?
🛑 When does it occur?
🛑 What are the symptoms?
🛑 How do we identify them?
🛑 What are ANOVULATORY CYCLES?
🛑 What causes it?
🛑 What can we do to prevent it?
WHAT IS OVULATION?
✅ Ovulation is simply the release of egg(s) from the ovary(ies).
✅ It is a part of the menstrual cycle of a woman and marks the middle of the cycle/ end of the first phase(follicular phase).
✅ Egg(s) released may or may not be fertilized. This means that not all ovulation will amount to pregnancy (obviously).
Note that for pregnancy to occur, ovulation must take place. No eggs, no pregnancy. Even if one undergoes assisted reproductive technology (ART), ovulation needs to have occurred somewhere before eggs can be harvested.
HOW DOES IT OCCUR?
✅ A girl is born with all her 1-2 million eggs (immature oocytes). Prior to puberty, she loses about 10,000 each month.
✅ At puberty, about 300,000 to 400,000 eggs remain. At this point the hypothalamus (a part of the brain) is mature enough to produce sex hormones. It releases GnRH which stimulates the pituitary gland (a small gland at the base of the brain) to release FSH which in turn now activates the ovaries to start maturing the follicles ( the little sacs in the ovaries containing the immature oocytes or eggs).
✅ Estrogen in the ovary then increases which makes the eggs to mature. About 1,000 eggs start the journey to maturity each month but only one usually succeeds.
✅ Once mature, another hormone, LH, causes the egg to be released from the ovary and voilà! ovulation has occurred!
✅ In some cases, more than one egg can be released either due to genetic factors or following medication. In rare cases, ovulation can occur more than once in a cycle.
The LH is also from the pituitary gland and it thins out the membrane covering the matured ovum(egg), enabling it to break out of the ovary.
▪️GnRH- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone
▪️FSH- Follicle Stimulating Hormone
▪️LH- Leutenizing Hormone.
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR?
✅ As stated, ovulation marks the middle of the cycle or the end of the follicular phase.
✅ Specifically, it occurs 2 weeks before the beginning of the next cycle. If someone can predict the beginning of the next cycle, you can predict ovulation day.
✅ Most women cannot predict their next period because each cycle can be influenced by other factors like diet, stress, illness, medication, etc. However it is important to note that is is usually towards the middle of the cycle so knowing your cycle length is important.
✅ Once the egg is released, it is alive for between 12 and 24 hours after which it dies off
✅ For pregnancy to occur, intercourse must not be only on the ovulation day. We can take advantage of the *Fertile Window*.
✅ The Fertile window is usually from about 5days leading to the ovulation day and up to 24hrs after actual ovulation. This is because sperm cells, under the right conditions, can live up to 5days.
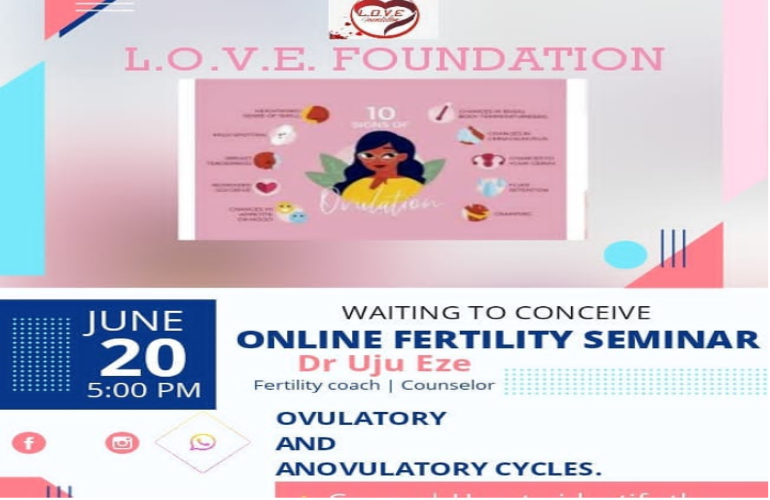
✅ To detect the actual ovulation day, tracking the symptoms is key.
1️⃣ Increase in vaginal mucus. Vaginal discharge becomes clear and stretchy (like raw egg white). After ovulation, the mucus clears and there’s a period of dryness before another discharge is seen which is cloudy, thicker and non stretchy. This is from studies and experience, the best method for self identification of the ovulation day proper. The mucus is seen for day(s) and on the day the mucus is not seen again is the actual ovulation day. Within the 24hrs of this day the mucus is not seen, the egg is released. This is important for sex selection.
2️⃣ Ovulation spotting/bleeding which is just tiny streaks of blood seen in the underwear after the egg is released.
3️⃣ Breast tenderness occurring sines days after menses. Not very reliable because breast tenderness can be caused by other factors like fondling, breastfeeding, mastitis, etc.
4️⃣ Increased libido/sex drive. Some women get very attractive during their fertile window and also have a higher urge for intercourse during the period. Again this can be influenced from other factors as well like state of emotions, stress level, etc.
5️⃣ Ovary pain aka mittleschmerz (in German) or middle pain. As the follicles mature, the stretching gives rise to the pain in the ovary from which the egg is to be released. The pain can start days before the actual rupture of the follicle and last some hours after. Not a specific determinant of the actual ovulation day.
6️⃣ Basal Body Tempreture (BBT). After the menses, the body temperature drips a little and then peaks slightly at ovulation before returning to normal. Keeping track of the BBT therefore can help one identify the ovulation day. This is best done in the morning before environmental factors affect body temperature. This also requires finesse as the temperature increase is very slight(0.2 or thereabouts) and can be missed.
7️⃣ Cervical position. At the beginning of the cycle, the cervix is firm, longer and closed. As ovulation approaches, it becomes softer, central and pulls up. It also becomes slightly open. This method of detecting ovulation is not usually encouraged for everyday people, except by examination from a medical practitioner.
8️⃣ Increased sense of smell. Some women at this time notice a sharper sense of smell. Remember that this is towards the middle of the cycle, some days after the period ends. Many don’t take note of it because they are not aware. Well now you know!😃😁.
9️⃣ Mood changes. Yes, due to the estrogen (happy hormone) some women are usually in a good mood days leading to ovulation. They are flirty and more playful. But beware! After ovulation occurs, progesterone increases which can be responsible for sour and aggressive mood, so your flirty playful lady today can become a tiger the next morning😂😂😂😱😨🤔🤣. Just understand with us.
1️⃣0️⃣ Fluid retention also occurs this period giving a feeling of increased weight or fullness in the body, but more in the breasts and stomach region, known as bloating. After ovulation, this regresses and can return just before the period so it can be confusing for some women.
HOW DO WE IDENTIFY OVULATION PERIOD
✅ It is important to note that ovulation is usually mid cycle. So in a woman with regular cycles (between 24 to 35 days) it will be anywhere from day 10 to day 21.
✅ This is wide. The first thing then is know YOUR OWN cycle length. Mark the days around 2weeks to the end of the cycle. Look out for the symptoms of ovulation on those days.
✅ So the best way to identify the fertile window is to listen to your own body.
✅ In summary it can be identified by knowing the middle of the cycle and looking out for the symptoms.
✅The surest way to identify ovulation is by ultrasound scan for follicular tracking. This is expensive and can be cumbersome to do monthly.
✅ Another method is by use of ovulation kits but this is not the best because it only tells us that the LH has been released but it does not guarantee that the egg was actually released as well.
✅ There are various ovulation apps now that basically uses the calendar method to detect when ovulation _*should*_ take place, but we have seen that other factors can influence ovulation taking place like stress, illness, diet, medication, etc so the app will not be accurate in these cases.
WHAT ARE ANOVULATORY CYCLES
✅ This is a cycle where ovulation does not occur. This means that a woman can be menstruating but ovulation is not taking place. So in such cycles, pregnancy cannot occur.
✅Anovulatory cycles are typified by unusual lengths. They can be </= 21days or >/= 35days. They can also occur in someone with usually regular cycles but when it occurs, there’s a delay in the period. It can delay for 5 or more day even up to 14days sometimes.
✅ Under normal circumstances every woman ovulates 13times a year. Sometimes ovulation skips under the following conditions:
WHAT CAUSES ANOVULATORY CYCLES
▪️Intracycle hormonal derangement leading to incomplete 2nd stage – follicle not ripening and egg not being released. This can be due to stress or diet.
▪️Gynaecological conditions like PCOS which suppresses sex hormones preventing their function.
▪️Other causes of hormone imbalance.
▪️Anovulatory cycles are “normal” in girls who have just started their periods(menache) and women who are approaching menopause (from 40 and above).
▪️Overweight and Underweight are also implicated in anovulation so maintaining a healthy BMI is important for proper ovulation.
Let us remember that LH is responsible for ovulation. Once the egg is released after the LH surge, progesterone raises to help the egg if it’s fertilized. If the egg is not fertilized, progesterone drops as well as estrogen and the period starts, another cycle begins. When there’s no LH surge, progesterone is still unavailable. This still looks like low or dropped progesterone level which will still cause the period so that’s how we have periods without ovulation. Also, drop in estrogen and the heavy endometrial lining where implantation didn’t occur, all lead to periods without ovulation. This explains the delay or shortened cycles and heavy flow in some cases of Anovulatory cycles.
So What Are the Symptoms and signs of Anovulatory cycles?
▪️Unusual cycle length
▪️Unusual delay in periods
▪️No symptoms of ovulation during the cycle
▪️Heavier periods in some cases
▪️Blood test will detect an abnormal progesterone level.
▪️Ultrasound will detect an unusual endometrial lining.
WHAT CAN WE DO TO PREVENT IT?
Like we have said, anovulation can be ‘normal’ in some cases like Menachem and peri-menopause. This cannot be controlled.
For anovulation due to medical/gynaecological conditions, treatment is tailored to the underlying condition.
For anovulation occurring in someone with otherwise regular cycles, the following can help regulate proper ovulation:
▪️Maintaining healthy BMI.
▪️ Proper exercise
▪️ Proper diet
▪️ Avoiding stress/ Practising relaxation techniques
▪️ Maintaining optimal health.
In summary, if from all we have learnt today you feel you are not ovulating, see your doctor. If you are cleared of any medical challenge, keep the above factors in check.

Leave A Comment